Efficient data storage is vital in today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where a colossal amount of data is being generated incessantly, necessitating secure and easily accessible storage solutions. In the following piece, we will embark on a journey to explore the diverse range of data storage options available, namely hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), and cloud storage. Each of these alternatives presents unique advantages and considerations, making it imperative to grasp their disparities to make well-informed decisions regarding your data storage requirements.
Hard drives have long reigned as a favored choice for data storage, offering a physical storage medium embedded within computer systems. They come in two primary types: hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). HDDs utilize spinning disks to read and write data, providing ample storage capacity at a relatively lower cost—conversely, SSDs leverage flash memory technology, resulting in swifter data access and enhanced performance. We will delve into the merits and limitations of hard drives, shedding light on the factors to consider when selecting the most suitable option to cater to your specific needs.
Furthermore, we will delve into network-attached storage (NAS), which permits centralized data storage accessible to multiple devices via a network. NAS devices offer many benefits, including data sharing, reliable data backup, and the convenience of remote access, rendering them an ideal solution for home and small business environments. Additionally, we will discuss NAS systems’ distinctive features and functionalities, providing valuable insights into their configuration and management.
Lastly, we will focus on cloud storage, which has witnessed a tremendous surge in popularity in recent years. Cloud storage entails storing data on remote servers accessed via the Internet. This storage solution offers unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and convenience, empowering users to access their data anywhere. However, it is crucial to carefully consider factors such as data security and privacy when opting for cloud storage. We will thoroughly examine the advantages and disadvantages of cloud storage and highlight noteworthy providers along with their key features.
Through an in-depth exploration of hard drives, NAS, and cloud storage, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of the available data storage solutions. Whether you find yourself as an individual, a small business owner, or a member of a larger organization, comprehending these options will undoubtedly facilitate well-informed decisions to meet your data storage needs efficiently and effectively.
Table of Contents
Understanding Hard Drives
Hard drives, a vital component of data storage solutions, serve as a tangible medium within computer systems for storing and retrieving digital information. These drives comprise spinning disks or platters that employ magnetic storage to facilitate swift and efficient access to stored data. Hard drives assume a pivotal role in data storage solutions by offering local storage options.
What Are Hard Drives?
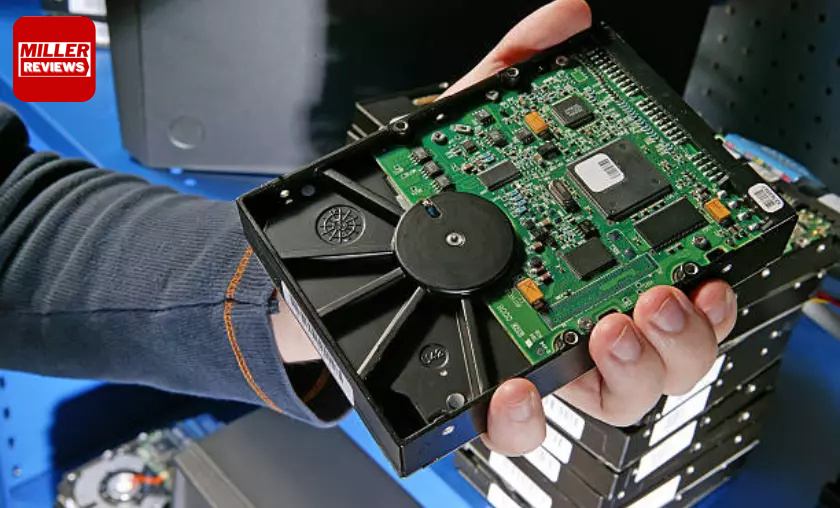

Hard drives present numerous advantages, contributing to their widespread adoption as a preferred choice for data storage. Primarily, they provide ample storage capacity, enabling users to house vast amounts of data, including documents, photos, videos, and applications. Additionally, hard drives offer cost-effectiveness compared to alternative storage solutions, rendering them an economical option for individuals and organizations. Furthermore, hard drives ensure persistent storage, safeguarding data integrity even when power is disconnected. This attribute proves crucial for applications necessitating long-term data retention.
Advantages And Limitations Of Hard Drives
Nevertheless, hard drives possess certain limitations. A notable constraint stems from their mechanical nature, incorporating moving components. Consequently, data access speeds may be relatively slower than alternative storage options such as solid-state drives (SSDs). Additionally, the mechanical components make hard drives more vulnerable to physical damage, reducing their durability. Furthermore, hard drives tend to consume more power and generate higher noise levels than SSDs.
Different Types Of Hard Drives (HDD, SSD)
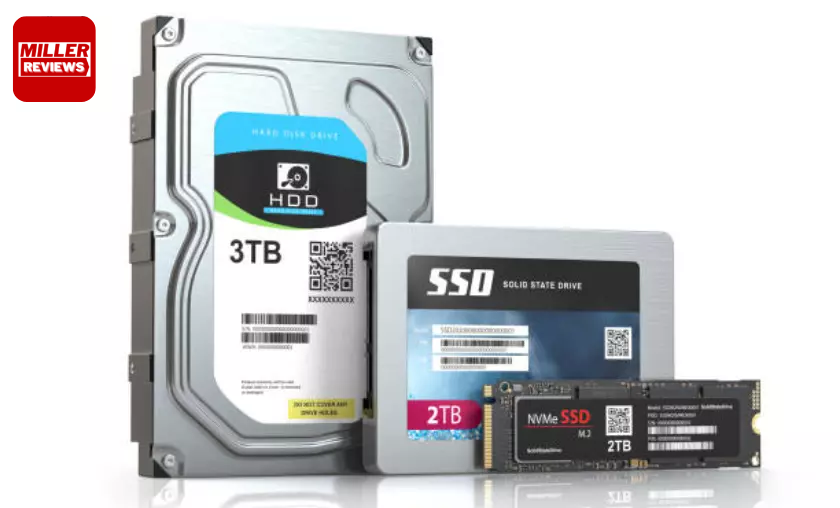

When selecting a hard drive, it becomes imperative to consider factors like storage capacity, performance, and reliability. The two primary types of hard drives are hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). HDDs employ spinning platters and read/write heads to access data, offering larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte. Conversely, SSDs utilize flash memory technology, delivering faster data access speeds, lower power consumption, and enhanced durability. When choosing a hard drive, essential factors include storage requirements, budgetary considerations, performance needs, and the intended usage scenario.
Factors To Consider When Choosing A Hard Drive
Comprehending the advantages, limitations, and distinct types of hard drives is pivotal in making well-informed decisions regarding data storage solutions. By carefully evaluating capacity, performance, and budget, individuals and organizations can select the most appropriate hard drive option that aligns with their specific storage requirements and intended use cases.
Exploring Network Attached Storage (NAS)
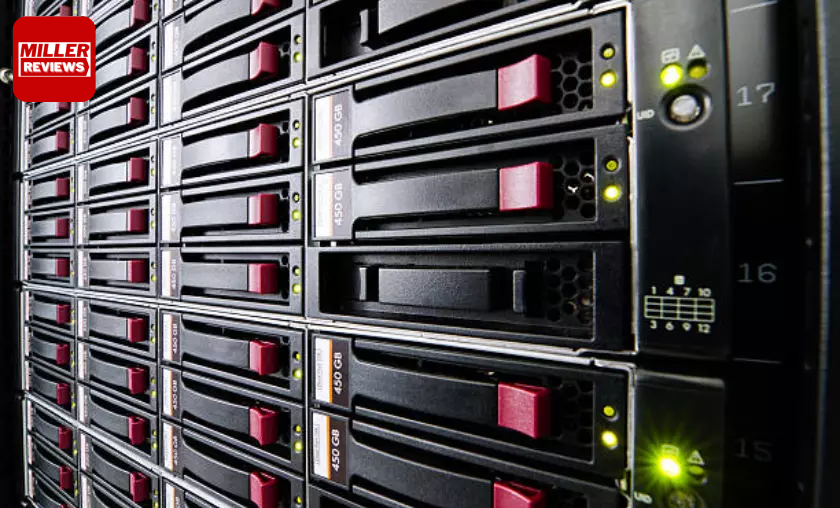

Network Attached Storage (NAS) presents an excellent data storage solution, enabling centralized storage accessible to multiple devices over a network. This dedicated device or storage server connects to a local area network (LAN) or a more significant network infrastructure. NAS operates on its operating system, offering file-level data storage that simplifies storing, retrieving, and sharing data across connected devices.
Benefits Of using NAS For Data Storage
A key advantage of using NAS for data storage lies in its centralized architecture. By employing NAS, users can store their data in a single location accessible to multiple users and devices concurrently. This eliminates the need for individual storage on each device, fostering efficient data management and collaboration. NAS also facilitates data sharing, empowering authorized users to access and collaborate on shared files and folders, enhancing productivity, and streamlining workflows.
Features & Functionalities Of NAS Devices
NAS devices boast many features and functionalities that make them versatile storage solutions. These include data redundancy and fault tolerance mechanisms, such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), ensuring data protection and availability even in the event of drive failure. Furthermore, NAS devices often provide advanced file management features like user access controls, file versioning, and remote access capabilities, enabling secure data access from anywhere. Some NAS devices offer additional functionalities like media streaming, backup services, and surveillance storage, providing comprehensive solutions for diverse storage needs.
Setting Up & Managing A NAS System

Setting up and managing a NAS system typically involves connecting the NAS device to the network, configuring network settings, creating user accounts, and establishing access permissions. NAS devices often feature user-friendly web interfaces or dedicated software that streamline system configuration and management. Administrators can customize settings, manage storage pools, create shared folders, and monitor system health and performance. Regular maintenance tasks such as firmware updates, backups, and security configurations are integral to NAS system management.
By delving into the capabilities of NAS, users can harness its centralized storage, data sharing, and advanced features to elevate data management, collaboration, and productivity. Whether for home or business use, establishing and managing a NAS system delivers a reliable and flexible data storage solution tailored to the requirements of multiple users and devices within a network environment.
Unveiling Cloud Storage
Cloud storage emerges as a dynamic data storage solution that entails storing and accessing data over the Internet on remote servers managed by cloud storage providers. It empowers users to store, manage, and retrieve data from any internet-connected device. Operating on a pay-as-you-go model, cloud storage enables users to scale their storage needs based on demand.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Cloud Storage

One of the primary advantages of cloud storage lies in its flexibility and scalability. Users can expand their storage capacity without additional hardware or infrastructure investments as data requirements grow. Cloud storage also offers convenient accessibility, enabling users to retrieve their data anytime, anywhere, using various devices. It facilitates file sharing and real-time collaboration features, supporting teamwork and remote work scenarios. Additionally, cloud storage providers often integrate data redundancy and backup features, ensuring data integrity and facilitating disaster recovery.
However, it is essential to consider the disadvantages associated with cloud storage. The reliance on internet connectivity means that accessing or uploading data may be affected if the connection is slow or unreliable. Users also depend on the cloud storage provider’s infrastructure and their ability to maintain service uptime and data security. Data security and privacy concerns arise as data is stored on remote servers managed by third-party providers. Moreover, ongoing costs may be incurred, as providers typically charge for storage capacity and additional features.
Popular Cloud Storage Providers & Their Features
Prominent cloud storage providers offer various features and options tailored to diverse user needs. Providers like Dropbox, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive ensure seamless integration with productivity tools, document collaboration features, and synchronization across multiple devices. Other providers, such as Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Storage, focus on delivering scalable and robust cloud storage solutions for businesses and developers, accompanied by advanced security and management features.
Ensuring Data Security & Privacy In The Cloud

Prioritizing data security and privacy in the cloud is crucial. Users should diligently evaluate the security measures implemented by their chosen cloud storage provider, including encryption, access controls, and data protection mechanisms. Understanding the provider’s data handling practices, ownership policies, and transfer protocols is paramount. Additionally, users should consider implementing their encryption measures and regularly backing up their data to mitigate the risks of data loss or unauthorized access.
Cloud storage offers convenience, scalability, and collaboration capabilities, rendering it an appealing data storage solution for individuals and organizations. By comprehending the advantages, disadvantages, and security considerations associated with cloud storage, users can make informed decisions when selecting a cloud storage provider and take necessary precautions to safeguard their data in the cloud.
Comparing Data Storage Solutions
When evaluating data storage solutions like hard drives, NAS, and cloud storage, it is crucial to consider multiple factors to make well-informed decisions. Performance and speed play a critical role in this evaluation. Hard drives, particularly solid-state drives (SSDs), deliver rapid data access speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring swift read and write operations. NAS devices can offer commendable performance, especially in network environments, facilitating simultaneous data access by multiple users. Cloud storage performance varies based on internet connection speed, but high-speed connections can provide efficient data access from anywhere.
Capacity & Scalability Considerations

Capacity and scalability considerations are also vital when comparing storage options. Hard drives, both HDDs and SSDs, provide ample storage capacities, with HDDs generally offering more fantastic accommodations at a lower cost per gigabyte. NAS devices allow for scalable storage expansion, enabling users to add more drives or upgrade storage capacity. Cloud storage offers unlimited scalability, as users can increase or decrease their storage space based on demand without concerns about physical limitations.
Cost Analysis Of Different Storage Options
Cost analysis is a pivotal aspect when evaluating storage solutions. Hard drives are often a cost-effective choice, particularly HDDs, as they offer high storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte. NAS devices involve upfront costs for the hardware, but the long-term costs can be relatively lower compared to other options due to their scalability and flexibility. Cloud storage typically operates on a subscription-based model, where users pay for the required storage space. It is essential to compare the costs of different cloud storage providers, considering factors such as storage capacity, additional features, and data transfer fees.
Use Cases For Each Storage Solution.

Understanding the use cases for each storage solution helps determine the most suitable option for specific requirements. Hard drives are ideal for individuals and businesses seeking local storage with high capacity and fast access speeds. NAS is perfect for environments with centralized data storage, collaboration, and accessibility across multiple devices and users. Cloud storage benefits those prioritizing convenience, remote access, and scalability, making it suitable for individuals, small businesses, and enterprises with distributed teams or varying storage needs.
Users can identify options that align with their specific requirements and priorities by comparing the performance, capacity, scalability, cost, and use cases of different data storage solutions. It is crucial to consider specific needs, budgets, and future growth plans to make informed decisions and select the most suitable storage solution.
Choosing The Right Data Storage Solution

Choosing the appropriate data storage solution demands a thorough assessment of your storage needs and careful consideration of various factors. To start, evaluating your storage requirements, including the amount of data you need to store, anticipated data growth, and performance expectations for your applications, is crucial. This understanding will guide your storage capacity, speed, and scalability evaluation.
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Storage Solution
Several factors should be taken into account when selecting a storage solution. These include cost, performance, reliability, ease of use, and security. Consider your budget and compare the prices associated with different upfront and ongoing options. Assess the performance characteristics of each solution, such as data access speed and latency, to ensure they align with your application requirements. Reliability is vital, so examine each solution’s durability and fault-tolerance features. Additionally, evaluate the ease of use, management capabilities, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
Combining Multiple Storage Options For Optimal Results
In certain situations, combining multiple storage options can yield optimal results. For example, combining hard drives, NAS, and cloud storage can create a comprehensive storage strategy. Local hard drives deliver fast, on-premises storage, while NAS provides centralized storage and collaboration within a network environment. Cloud storage enables remote access, scalability, and off-site backups. By leveraging these solutions together, you can customize your storage architecture to meet your specific needs while capitalizing on the unique advantages of each option.
Planning For Data Backup & Redundancy

Data backup and redundancy should always be a top priority. Regardless of the chosen storage solution, implementing a robust backup strategy is essential to safeguard against data loss. Regularly perform backups to a secondary storage medium, such as an external hard drive or cloud backup service, to ensure data integrity and resilience. Redundancy measures, such as RAID configurations or data replication, can enhance data availability and protect against hardware failures. Make data backup and redundancy integral components of your storage solution to mitigate the risk of data loss and maximize data security.
You can make an informed decision when selecting the proper data storage solution by evaluating your storage needs, considering critical factors, exploring multiple storage options, and prioritizing data backup and redundancy. Each organization or individual may have unique requirements, and by carefully assessing these factors, you can identify the storage solution that best aligns with your needs, budget, and long-term storage strategy.
Future Trends In Data Storage

The data storage landscape is constantly evolving, driven by emerging technologies that bring forth new possibilities and advancements. One significant trend in this field is the development of cutting-edge technologies like solid-state drives (SSDs) with higher capacities and faster speeds. Due to their superior performance characteristics, SSDs gradually supplant traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). Furthermore, the adoption of technologies such as non-volatile memory express (NVMe) and storage-class memory (SCM) is being embraced further to enhance the speed and efficiency of data storage solutions.
Impact Of Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are also pivotal in shaping the future of data storage. These transformative technologies enable intelligent data management, predictive analytics, and automated storage optimization. AI and ML algorithms can analyze patterns in data usage, predict future storage requirements, and optimize storage allocation based on workload demands. This results in improved storage efficiency, cost reduction, and performance enhancement. Moreover, AI and ML find applications in data deduplication, data compression, and data security, providing advanced solutions for efficient data management and protection.
Predictions For The Future Of Data Storage
Several predictions can be made regarding the future of data storage. Firstly, adopting cloud storage is expected to continue its upward trajectory as more businesses and individuals recognize its flexibility, scalability, and convenience. However, hybrid solutions that combine on-premises and cloud storage will likely gain prominence, allowing for a balanced performance, security, and cost-effectiveness approach. The rise of edge computing, where data is processed closer to its source, will also drive the demand for decentralized storage solutions and edge storage devices.
Furthermore, technological advancements such as holographic, DNA, and quantum storage are on the horizon. These innovations hold the potential for even higher storage densities, longer-term data retention, and enhanced data security. Although these technologies are still in the research and development phase, they present promising prospects for the future of data storage.
As technology evolves, individuals and organizations must remain informed about these trends and adapt their data storage strategies accordingly. By embracing emerging technologies, harnessing the power of AI and ML, and anticipating future developments, data storage solutions can meet the ever-increasing demands of the digital world. This proactive approach unlocks new possibilities for efficient, secure, and scalable data storage.
Best Practices For Data Storage Management
Effective data storage management is paramount to safeguard the integrity, security, and accessibility of your valuable data. Adhering to best practices can optimize your storage systems and ensure efficient data management.
Organizing & Categorizing Your Data

A foundational step in data storage management is organizing and categorizing your data. Establish a logical structure for storing and managing files and folders. Employ consistent and descriptive naming conventions to facilitate easy identification and retrieval of data. Categorize data based on type, purpose, or relevance to specific projects or departments. Implement metadata, such as tags or keywords, to enhance searchability and organization. Regularly review and declutter your storage systems, removing outdated or unnecessary data to improve performance and free up storage space.
Implementing Data Backup Strategies
Implementing data backup strategies is critical to safeguard against data loss. Develop a robust backup plan that includes regular and automated backups of essential data. To ensure data availability during hardware failures or disasters, utilize redundant storage systems, such as RAID configurations or off-site backups. Periodically test your backup and recovery processes to validate their effectiveness. Consider implementing a combination of local backups, such as external hard drives, and off-site or cloud backups for comprehensive data protection.
Ensuring Data Integrity & Reliability
Ensuring data integrity and reliability is another vital aspect of data storage management. Regularly monitor the health of your storage devices and be vigilant for signs of degradation or potential failures. Implement data validation techniques, such as checksums or error correction codes, to detect and rectify data corruption. Employ reliable storage media and regularly update firmware or software to maintain optimal performance and security. Implement access controls and encryption mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Regular Maintenance & Monitoring Of Storage Systems

Regular maintenance and monitoring of storage systems are critical to identify and address potential issues proactively. Monitor storage capacity and performance to ensure efficient utilization and plan for future growth. Regularly update and patch your storage system’s firmware or software to benefit from bug fixes, security enhancements, and performance optimizations. Monitor storage health metrics, such as temperature, disk health, or storage array performance, to proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact data integrity or system performance.
By implementing these best practices for data storage management, you can ensure the organization, protection, and reliability of your data. Efficient storage management enables easy data retrieval, reduces the risk of data loss, and maintains optimal performance, ultimately contributing to your organization’s overall success and productivity.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples

Analyzing real-world case studies provides valuable insights into successful data storage implementations. Case studies from different industries highlight industry-specific use cases and the benefits of various storage solutions such as hard drives, NAS, and cloud storage. For instance, in the healthcare industry, the adoption of NAS has improved centralized data storage and secure access to patient records, enhancing patient care and collaboration. On the other hand, cloud storage has been widely adopted by technology companies for data backup and collaboration, enabling seamless teamwork and scalability.
These case studies offer important lessons and best practices. Understanding industry-specific needs is crucial when selecting the appropriate storage solution, considering each sector’s unique challenges and compliance requirements. Implementing robust data security measures, including encryption and access controls, is vital to safeguard sensitive information. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and backup strategies are essential for ensuring data integrity and availability. By studying real-world case studies, organizations can gain practical insights into successful data storage implementations, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their storage solutions accordingly.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of Data storage solutions, we have delved into the distinctive features, advantages, and considerations associated with hard drives, NAS, and cloud storage. Each option offers its benefits and caters to different storage requirements. To recap, hard drives excel in high-capacity storage and fast data access, while NAS devices provide centralized storage and collaboration capabilities within a network environment. On the other hand, cloud storage stands out with its scalability, remote accessibility, and convenience.
To make an informed decision and choose the appropriate storage solution for your specific needs, it is vital to assess your requirements thoroughly. Consider data volume, performance needs, scalability, budget, and security. Analyze your use cases and determine whether you require local storage, centralized storage within a network, or the flexibility and scalability offered by cloud storage. By clearly understanding your specific needs, you can select a storage solution that aligns with your priorities and fits your budget.
Selecting the proper data storage solution entails a comprehensive evaluation of each option’s advantages and limitations, alongside considering your unique requirements. Assessing multiple factors such as performance, capacity, scalability, cost, and data security is advisable. Additionally, drawing insights from industry best practices, studying real-world case studies, and staying informed about emerging trends can help guide your decision-making process. By diligently evaluating your needs and considering all relevant factors, you can confidently choose the storage solution that best suits your requirements, ensuring efficient and reliable data storage for your personal or organizational needs.
For More amazing articles related to Tech Check out our website Over Here
To Read more similar articles click here
Thanks for visiting our Website. If you appreciate our work, kindly show us some support in our comments section 🙂